Task management in RTFP¶
Overview¶
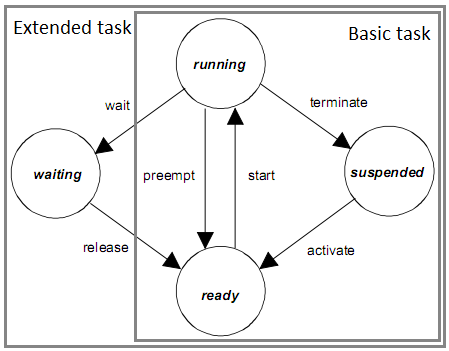
In real time multi-core systems, it is essential to realize separate tasks that perform -usually- independent actions. RTFP follows the OSEK standard to manage tasks.
Since it was based on FreeRTOS, RTFP has the semantics of OSEK within the FreeRTOS kernel, with different names
- Running
- Waiting
- suspended
- Ready
For more detailed description of task state model, refer to the OSEK specifications. This diagram shows the transition between task states.
RMS task scheduling¶
RTFP will schedule tasks according to RMS (Rate Monotonic Scheduling) policy by default.
Resterictions when using RTFP with RMS scheduling:
- priorities of all tasks are unique.
- the task with the smallest period must have highest priority.
- Priorities decrease by 1 each time for the other tasks depending on peiorities.
- Highest priority is number of all tasks running on a core.
Fixed priority task scheduling¶
As mentioned elsewhere, RTFP is based on FreeRTOS, and therefore, the original scheduling policy of FreeRTPOS could be used to manage tasks. FreeRTOS uses fixed priority schedling. In order to use this schedling, it is simply required to alter the priority scheme used for the tasks. While RMS requires all the tasks to have unique, monotonically increasing (or decreasing priorities), Fixed priority scheduling does not require such restrictions, multiple tasks could have the same priority, and different priorities are not assigned based on a task’s period but is left for the descretion of the developer using RTFP.
Creating tasks using RTFP¶
To create a task in RTFP, first initialize an amaltheaTask struct as follows
AmaltheaTask createAmaltheaTask(void *taskHandler,
void *cInHandler,
void *cOutHandler,
unsigned int period,
unsigned int deadline,
unsigned int WCET);
arguments:
- taskHandler : pointer to the function that contains task code
- cInHandler : pointer to the function that creates a copy of shared varialbles (labels) on the task stack. This function will be called at the beginning of every new instance of a task.
- cOutHandler : pointer to the functions that returns the local copy of shared variables into shared memory. (write operation).
- period : period of the task in ticks
- deadline : relative deadline in ticks
- WCET : Worst Case Execution Time in ticks.
This function will return a struct of type AmaltheaTask. This struct will be used to create an RTOS task as follows:
void createRTOSTask(AmaltheaTask* task,
int priority,
int argCount,
...);
Arguments:
- task : pointer to the AmaltheaTask struct
- priority : priority of the task (according to RMS, lowesrt perio has highest priority)
- argCount : number of different types of labels used by this task
- label_type_size : size (in bits) of label type.
- label_type_count: number of labels associated with that type.