Distributed shared memory management in RTFP¶
Overview¶
Each core on the Epiphany processor has independent local memory which is accessible by other cores on the epiphany chip as well as the host AR< processor, and hence it can be regarded as distributed shared memory. This ditributed shared memory will be used to store variables (labels) that are shared between tasks. Additionally, it will be accessed regularly by the host ARM processor to get the status of the core and information on its operation at any given point in time.
shared variables (labels) are allocated in the distributed shared memory statically.
The labels are grouped together by size in contiguous memory blocks called “sections”.
Distributed shared memory model¶
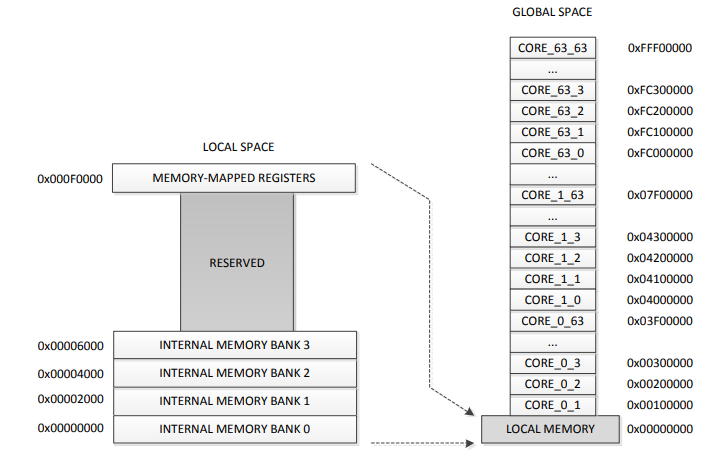
User accessible memory address space on core ranges from core_address + 0x0000 to address core_address + 0x7FFF with core_address referring to the start address of the core in the global address space, within this address space, all shred labels should assigned. This memory is divided into 4 memeory banks. Access to those memory banks can be restricted individully.
This figure shows the memory model of Epihany cores, the memory map is explained in more detail here.
All labels of the same type will be allocated to an array of that type. Accessing those labels can be done by simply accessing the index of the array.
Distributed shared memory initialization and allocation in RTFP¶
Each distributed shared memory section will be initialized individually. If the code using RTFP is automatically generated, initialization function should be called for each section individually.
To intialize a new shared memory section in RTFP, the following steps are required:
- Declare a struct of the type
DSHM_sectionthat contains the attributes of the memory section such as base address (relative to the core address space), nummber of labels, data type of the labels, and the row and column of the core where this memory is allocated. This struct is defined in RTFP as follows:
struct{
unsigned row;
unsigned col;
unsigned int base_addr;
unsigned label_count;
TYPE sec_type;
}typedef DSHM_section;
For instant, a section of 10 labels is declared on core (0,0) with the base address of this section at 0x4000 as follows:
DSHM_section sec1_core_00 = {0,0,0x4000,10};
Note that even though the section type sec_type is a field of the struct DSHM_section, it can be omitted from the struct declaration, which indicates that the data type of this section is the default data type unsigned int.
- Allocate the declared memory section in the distributed shared memory by calling the function
DSHM_section_init, example:
DSHM_section_init(sec1_core_00);
The return type of this function is void. It does not return a pointer to the memory section as is the case with shared memory. The reason for this is to allow for a more compact code that does not require calling this function to initialize a section on a core from multiple cores (including that core itself) in order to acquire the pointer to this section. This issue will be fixed by the next release of RTFP parallella such that a core can notify other cores on the epiphany chip of the existence of the section being initialized. This will simplify the process of distributed shared memory access accross cores. The current procedures for accessing such memory is described below.
shared memory access in RTFP¶
Declared memory sections in RTFP are pointers to actual memory addresses. In order to write to a given label in a section, the relative address in the core will be given by the index and that will be added to the base address of the core memory to find the absolute address of the variable (label) to be written.
unsigned int *addr;
unsigned int* addr_base;
addr_base = get_base_address_core(row,col);
addr = (unsigned int*) ((unsigned ) addr_base | (unsigned)outbuf_dstr_shared[label_indx]);
*addr = payload;
Similarly to read the label:
unsigned int *addr;
unsigned int* addr_base;
addr_base = get_base_address_core(row,col);
addr = (unsigned int*) ((unsigned ) addr_base | (unsigned)outbuf_dstr_shared[label_indx]);
return *addr;
Where *addr will return the value at the requested label_indx.
In order to access the declared memory section anywhere in the project, the functions write_DSHM_section and read_DSHM_section can be used, in a similar way to accessing the sharede memory.
uint8_t write_DSHM_section(DSHM_section sec,int label_indx,int payload);
unsigned int read_DSHM_section (DSHM_section sec, int label_indx);
where sec is the struct that contains the section attributes, label_indx is the index of the label relative to the beginning of the section, and payload is the value to be written to memory (if any).
The read function currently returns the value stored in the memory address as an unsigned int by default. This will be changed in the next release of RTFP to allow for returning a type that is conformant with the memory section data type.